As a necessary component of over 325 biochemical reactions, magnesium is one of the most important essential nutrients for maintaining optimal health and performance.
Magnesium plays a role in vital processes such as protein syntheses, cardiovascular health, immune function, and blood sugar management. Specific to the brain, magnesium promotes healthy neuronal activity for supporting recall, learning, decision making, and spatial recognition.
It’s impossible to achieve optimal mental and physical performance without maintaining proper levels of magnesium.
Unfortunately, magnesium is one of the most deficient minerals in the American diet. In fact, the percentage of the U.S. population deficient in magnesium could be as high as 80%. Deficiency can lead to “brain fog” and disease.
INTRODUCING MAGTECH™ - THE OPTIMAL MAGNESIUM COMPLEX
MagTech™ is a premium blend of all three different types of magnesium known to have the highest absorption, Magtein Magnesium L-Threonate, Magnesium Taurate, and Magnesium Glycinate.
Each compound is fully chelated for optimal absorption and effectiveness. “Chelated” means that the magnesium is bonded to an amino acid. Chelation is the body’s natural means to transport minerals across the intestinal wall as part of digestion, so chelated magnesium is far better absorbed than most supplements which are cheap magnesium salts.
MagTech™ has 100% nutritional density, meaning that all components of the magnesium complex have true nutritional value. We carefully chose forms of magnesium that are chelated with nutritionally functional amino acids, each with a specific role to optimize mental and physical performance.
Magtein™ Magnesium L-Threonate & Synapse Density
The human brain has about 100,000,000,000 neurons that communicate with each other through synaptic connections. Each individual neuron is capable of having thousands of synapses, leading to trillions of synaptic connections in the brain. These connections create neural networks that form the foundation for higher cognitive functions like learning, memory, and emotional regulation.
The more synaptic connections you have, the better your memory, the faster your brain processes information, and the better your attention and focus will be.
A breakthrough discovery at MIT demonstrated the key role that magnesium plays in regulating synapse density. The team of scientists showed that increasing magnesium levels in the brain leads to a significant and lasting increase in the number of functional synapses. However, the scientists found that conventional magnesium supplements were very poorly absorbed and failed to elevate magnesium in the brain, so they developed Magtein™.
Magtein™ is a proprietary magnesium compound specifically designed to increase brain magnesium levels. It is a form of magnesium that is chelated to L-threonate (a metabolite of vitamin c) to act as a carrier to facilitate magnesium’s entry into the brain.
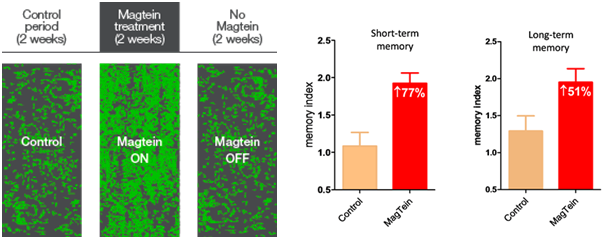
Magtein™ (magnesium l-threonate) has been shown to significantly increase the brain’s number of synaptic connections / synaptic density (see graph on the left), and enhance both short-term and long-term memory (see graph on the right).
Magnesium Taurate & Neurotransmitter Balance
Magnesium taurate delivers an important amino acid, taurine to the brain and body. Magnesium and taurine have synergistic and potentiating roles.
Magnesium and taurine work together to stabilize cell membranes throughout the central nervous system and maintain neurotransmitter balance. One of taurine’s main tasks is to facilitate the passage of sodium, potassium, and magnesium ions into and out of cells for optimal neuronal activity.
Taurine has a role in vision, cardiac health, bile production, as well as muscle growth. It also acts as an antioxidant, inhibiting LDL cholesterol oxidation.
Magnesium Glycinate & Sleep Quality
Magnesium glycinate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium and a significant source of glycine, an amino acid that promotes deep sleep and the elimination of toxins from the body.
Magnesium and glycine both have a calming effect on the brain, helping to reduce stress and increase sleep quality. Restful sleep is important for the restoration of energy stores in brain cells depleted during a full day of thinking. And with it’s anti-inflammatory properties, glycine is beneficial to the entire recovery process.
Glycine has been shown to improve memory retrieval and reduce fatigue in individuals with sleep-depriving conditions, including jet lag and overwork.
As an essential component in the synthesis of creatine, glycine also helps preserve muscle mass and prevent liver damage. It plays a key role in liver detoxification by increasing glutathione.
Accelerate your mind with 
Suggested Use: Take 2 servings per pay, preferably 1 serving in the afternoon and 1 serving in the evening, or as directed by a healthcare practitioner.
U.S.A manufactured in a GMP facility. Natural Stacks proudly uses only the highest quality ingredients.
Magtein™ Magnesium L-Threonate
Built on over a decade of research, scientists from MIT (including a Nobel Prize laureate) developed the revolutionary new compound Magtein™ (magnesium l-threonate) to increase the levels of magnesium in the brain for optimal mental function, memory, and sleep.
"Magtein™ is a trademark of Magceutics, Inc. and is distributed exclusively by AIDP, Inc. Magtein is covered by registered and pending U.S. Patents."
Magnesium Taurate
Magnesium Taurate is a synergistic combination of magnesium and taurate, a free-form amino acid. It’s known to decrease anxiety, relieve muscle fatigue, and promote a stronger immune system. This form of magnesium supports maximum absorption in the cells and distribution throughout the body.
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate has a positive impact on attention, memory, and stress reduction. Utilizing the essential amino acid glycine, this form of magnesium has a calming effect on the brain and promotes deeper sleep.
Magnesium L-Threonate:
In a recent rodent study, top neuroscientists from universities in Beijing, Texas, and Toronto found that “elevation of brain magnesium, by a novel magnesium compound [magnesium-l-threonate (MgT)], enhances synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus and learning and memory” [1]
Twelve scientists at MIT conducted a study on magnesium-L-threonate and concluded that “an increase in brain magnesium enhances both short-term synaptic facilitation and long-term potentiation and improves learning and memory functions.” [2]
A study using magnesium-L-threonate to treat Alzheimer’s Disease discovered that “Elevation of Brain Magnesium Prevents and Reverses Cognitive Deficits and Synaptic Loss” [3]
In early 2014, two human studies on magnesium-L-threonate will be released to the public.
Taurine (found in Magnesium Taurate):
Researchers at Tufts University found that "Taurine increased choice reaction time" and "Taurine reversed the effects of caffeine-withdrawal symptoms" [4]
A recent study on taurine's neuroprotective properties concluded that taurine supplementation "significantly ameliorated the age-dependent decline in spatial memory acquisition and retention" and can "forestall the age-related decline in cognitive functions". [5]
In Japan, a study of 25 male college students found that "taurine supplementation alleviates visual fatigue induced by visual display terminal (VDT) work" [6]
Glycine (found in Magnesium Glycinate):
A 2012 study on healthy male volunteers found that "glycine improves daytime sleepiness and fatigue induced by acute sleep restriction" [7]
A study on individuals with continuous complaints about the quality of their sleep concluded that "glycine ingestion significantly improved the following elements: 'fatigue', 'liveliness and preppiness', and 'clear-headedness'." [8]
When studying the effects of glycine ingestion before bedtime on volunteers who have been experiencing unsatisfactory sleep, scientists in Japan found that it "improved the volunteers' satisfaction with their sleep, the difficulty of sleep onset, and sleep efficiency" [9]
Sources:
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22016520
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20152124
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23658180
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22819803
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23963537
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14752617
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22529837
- http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1479-8425.2006.00193.x/abstract
- http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1479-8425.2007.00262.x/abstract


















